قانون الضريبة على الدخل وفقاً لآخر تعديل صادر فى 15 يونيو 2023
مدونة مجانية غير هادفة للربح تهتم بنشر العلم في مجال الضرائب والقانون المصري واالمحاسبة والمراجعة والهدف المنشود محاولة تنظيم الكم الضخم من المعلومات المحاسبية والضريبية على الانترنت للتيسير على الباحثين
Excel functions are the backbone of a financial modeler’s day to day work and as such, it’s essential to have a good understanding of the functions that are commonly used to build financial models.
Below are the top Excel functions that you must know as a financial modeler grouped by area.
Are there any functions that you would include in your top 20 functions for
In Microsoft Excel, the CHOOSE function selects a value or performs an action from a list of values, based on the index number. It needs two required arguments to function.
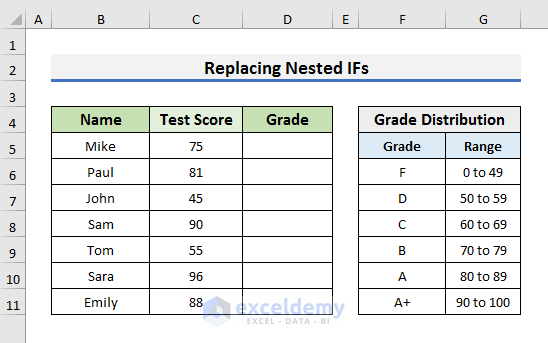
Use Excel CHOOSE Function to Replace Nested IFs
In the first case, we will return a value based on some conditions using the CHOOSE function. The dataset we will use here contains the Test Scores of some students. We can easily assign the grades using the CHOOSE function. You can see the Grade Distribution in the picture below.
In Microsoft Excel, the CHOOSE function selects a value or performs an action from a list of values, based on the index number. It needs two required arguments to function.
CHOOSE(index_num, value1, [value2]….)
index_num: It is the position number of the values. Position of value1 is 1, value2 is 2, and so on.
value1: It is the second required argument inside the CHOOSE function. You can enter value2, value3, and many more for your purposes.
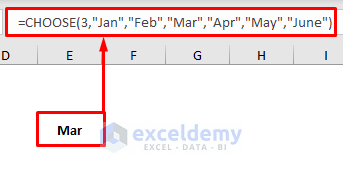
For example, if you type =CHOOSE(3,"Jan","Feb","Mar","Apr","May","June") in a cell, and, press Enter, then the output will be Mar because Mar is the third value among the specified values.
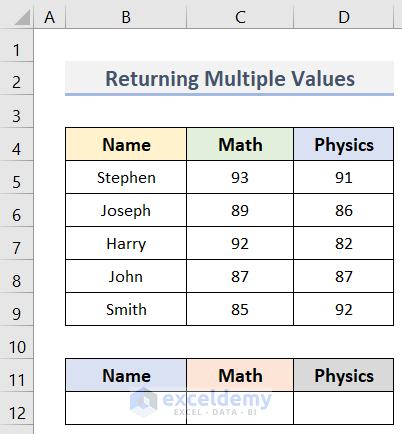
Apply CHOOSE Function with Array to Return Multiple Values in Excel
Let’s say, we have a dataset (B4:D12) in Excel containing the Names of some students and their marks in Math and Physics. However, we need to pick a student’s Name along the marks in the two subjects. Here, we will use the CHOOSE function in Excel with the array to return these multiple values. By applying the formula of this method, we will always get the values in a row even if they are in a column. The steps are below.
Using CHOOSE Function along with VLOOKUP in Excel
In Excel, managing space is a very important point to consider. Now, let’s suppose you are in a situation where you want to compare multiple columns in the Excel dataset, and you want to derive results, This is not possible using the VLOOKUP function alone. So, to make a function capable of doing something like this, we will introduce a special function known as CHOOSE function. But, if you don’t want to use CHOOSE function, then you have to use a helper column, making the job a little hectic.
So, in this article, we will see how to use VLOOKUP along with CHOOSE function.
First, we will see the syntax of CHOOSE FUNCTION in brief.
CHOOSE FUNCTION:
Syntax:
CHOOSE(ARRAY DIMENSIONS(INDEX VALUE(S)),VALUE(1),VALUE(2),VALUE(3),.....)
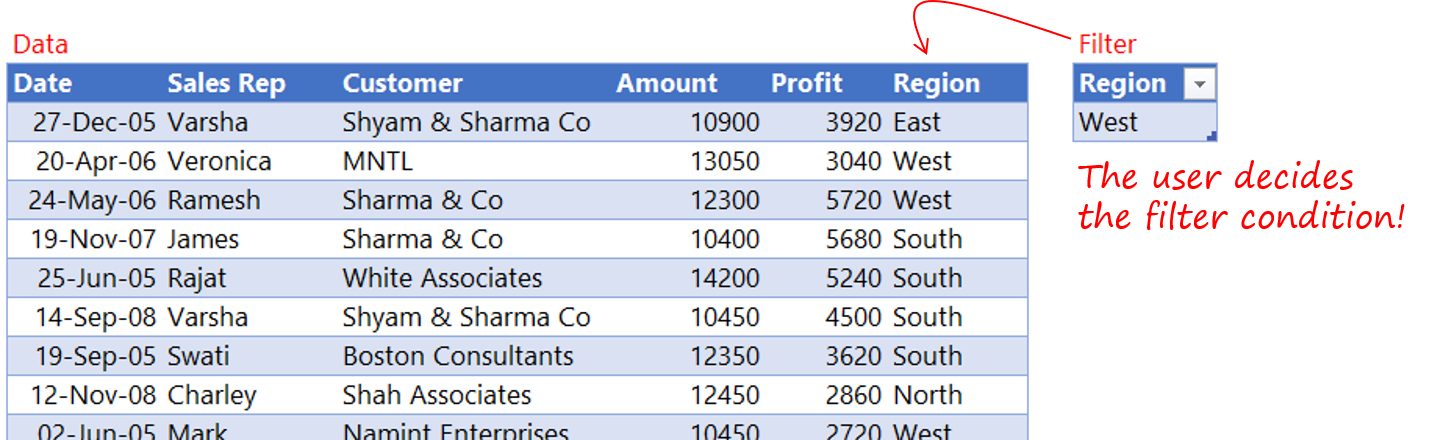
Let’s say you would like to filter the Region Column in your data by the value the user inputs in a cell
Assuming that you know how to load the Data (both tables) in Power Query, let’s see what
Excel OFFSET Function for Dynamic Calculations
Excel OFFSET Function for Dynamic Calculations
Do you want to create formulas that “move” with your raw data set?
That’s when you need to use Excel’s OFFSET function.
OFFSET is a great formula whenever you have dynamic ranges involved. Some examples are:
Calculating the average of the last three months when you add new data to your table
Getting data from the last cell in your raw data range – either last row or last column in that range
Grabbing data from a data table based on a point of view chosen by the user
Complex calculations that require “moving” data sets
3 Practical cases of Excel OFFSET are shown in this Video:
حساب ضريبة المرتبات بعد تعديل قانون الدخل رقم 92 لسنة 2005 بالقانون رقم 30 لسنة 2023
عن طريق كود M باداه Power Query
--------------------------
if [المرتب السنوي] <= 21000 then 0
else if [المرتب السنوي] <= 30000 then ([المرتب السنوي]-21000)*0.025
else if [المرتب السنوي] <= 45000 then ([المرتب السنوي]-30000)*0.1+225
else if [المرتب السنوي] <= 60000 then ([المرتب السنوي]-45000)*0.15+1725
else if [المرتب السنوي] <= 200000 then ([المرتب السنوي]-60000)*0.20+3975
else if [المرتب السنوي] <= 400000 then ([المرتب السنوي]-200000)*0.225+31975
else if [المرتب السنوي] <= 600000 then ([المرتب السنوي]-400000)*0.25+76975
else if [المرتب السنوي] <= 700000 then ([المرتب السنوي]-600000)*0.25+127500
else if [المرتب السنوي] <= 800000 then ([المرتب السنوي]-700000)*0.25+154750
else if [المرتب السنوي] <= 900000 then ([المرتب السنوي]-800000)*0.25+182000
else if [المرتب السنوي] <= 1200000 then ([المرتب السنوي]-900000)*0.25+210000
else if [المرتب السنوي] > 1200000 then ([المرتب السنوي]-1200000)*0.275+300000
الضريبة على القيمة المضافة المستحقة على الآلات والمعدات الواردة من الخارج للمصانع والوحدات الإنتاجية لإستخدامها فى الإنتاج الصناعى أو إنتاج سلعة أو تأدية خدمة.